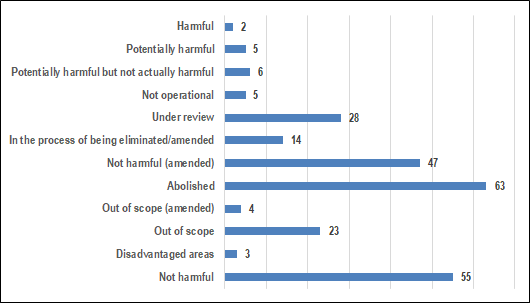
- Real GDP growth is projected at 3.8 percent in 2018 and 3.9 percent in 2019, driven by robust performance in the financial services, construction, and tourism sectors.
- Mauritius faces the challenge of boosting inclusive economic growth while preserving fiscal sustainability, regaining external competitiveness, and maintaining financial integrity.
- The mission welcomed the authorities’ ongoing efforts to strengthen the AML/CFT framework and reiterated the need for maintaining strong and independent institutions to overcome the policy challenges Mauritius faces to remain an attractive investment destination.
An International Monetary Fund (IMF) mission led by Mahvash Qureshi visited Mauritius during January 16–30, 2019 to conduct the discussions for the 2019 Article IV consultations.
At the conclusion of the visit, Ms. Qureshi issued the following statement today in Port Louis:
“The Mauritian economy continues to grow at a steady pace, benefiting from a vibrant services sector and strong domestic demand. Real GDP expanded by 3.8 percent in 2017 and is projected to grow at a similar rate in 2018. Inflationary pressures have receded, and the unemployment rate has fallen to its lowest level in a decade. The external balance, however, continues to deteriorate due to a rising trade deficit in goods. The fiscal deficit in FY2017/18 was about 0.3 percent of GDP lower than budgeted, with public sector debt decreasing to 63.7 percent of GDP at the end of the fiscal year from 65.0 percent of GDP in FY 2016/17. Activity in the offshore global business sector has remained broadly resilient while reforms to the sector are underway. A prudent stance by financial services firms and supervisory agencies has helped to maintain financial stability.
“The growth momentum is expected to continue in 2019. Real GDP growth is projected to reach 3.9 percent in 2019, driven by robust performance in the financial services, construction, and tourism sectors. With international oil prices expected to decline in 2019, inflation is projected to drop further, while the current account deficit is expected to widen to about 7 percent of GDP owing to higher capital imports associated with large-scale public infrastructure projects. Given the expansionary fiscal stance in FY2018/19 and external borrowing to finance public investment in infrastructure, public sector debt is projected to increase.
“Going forward, the key challenge for Mauritius is to boost inclusive economic growth, while preserving fiscal sustainability, regaining external competitiveness, and maintaining financial integrity and stability. To preserve macroeconomic stability, especially in view of the rapidly aging population, and to create room to respond to shocks, the mission advised the authorities to adopt prudent fiscal policies that would set public sector debt firmly on a declining path into the medium term. The monetary policy stance is broadly appropriate at the current juncture. However, given the upside risks to inflation, vigilance is warranted against any emerging inflationary pressures.
“A range of reforms and initiatives has been introduced in recent years to spur productivity and competitiveness—including the adoption of the Business Facilitation Act, finalization of the Financial Sector Blueprint, and programs to support youth skill development, small-scale entrepreneurs, and female labor force participation. Improvement in the World Bank’s Doing Business 2019 indicator is encouraging. Coordination and synergies between the various reforms and initiatives, as well as interaction among the stakeholders, could however be strengthened to enhance their effectiveness and efficiency.
“The mission welcomed the authorities’ ongoing efforts to strengthen the AML/CFT framework in line with the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations and reiterated the need for maintaining strong and independent institutions to overcome the range of policy challenges Mauritius faces to remain an attractive investment destination.
“The mission team expresses its gratitude to the authorities for the productive discussions, excellent cooperation, and hospitality. The IMF stands ready to assist the authorities in the implementation of their economic program, including through the provision of technical assistance, and looks forward to continuing fruitful policy dialogue.”
The mission met with the Prime Minister and Minister of Finance and Economic Development, Pravind Jugnauth, Minister of Financial Services, Good Governance and Institutional Reforms, Dharmendar Sesungkur, Governor of the Bank of Mauritius Yandraduth Googoolye, the Financial Secretary, Dharam Dev Manraj, and other senior government officials, as well as the opposition leader, representatives of the private sector, academia, civil society, unions, and the donor community.
At the conclusion of the visit, Ms. Qureshi issued the following statement today in Port Louis:
“The Mauritian economy continues to grow at a steady pace, benefiting from a vibrant services sector and strong domestic demand. Real GDP expanded by 3.8 percent in 2017 and is projected to grow at a similar rate in 2018. Inflationary pressures have receded, and the unemployment rate has fallen to its lowest level in a decade. The external balance, however, continues to deteriorate due to a rising trade deficit in goods. The fiscal deficit in FY2017/18 was about 0.3 percent of GDP lower than budgeted, with public sector debt decreasing to 63.7 percent of GDP at the end of the fiscal year from 65.0 percent of GDP in FY 2016/17. Activity in the offshore global business sector has remained broadly resilient while reforms to the sector are underway. A prudent stance by financial services firms and supervisory agencies has helped to maintain financial stability.
“The growth momentum is expected to continue in 2019. Real GDP growth is projected to reach 3.9 percent in 2019, driven by robust performance in the financial services, construction, and tourism sectors. With international oil prices expected to decline in 2019, inflation is projected to drop further, while the current account deficit is expected to widen to about 7 percent of GDP owing to higher capital imports associated with large-scale public infrastructure projects. Given the expansionary fiscal stance in FY2018/19 and external borrowing to finance public investment in infrastructure, public sector debt is projected to increase.
“Going forward, the key challenge for Mauritius is to boost inclusive economic growth, while preserving fiscal sustainability, regaining external competitiveness, and maintaining financial integrity and stability. To preserve macroeconomic stability, especially in view of the rapidly aging population, and to create room to respond to shocks, the mission advised the authorities to adopt prudent fiscal policies that would set public sector debt firmly on a declining path into the medium term. The monetary policy stance is broadly appropriate at the current juncture. However, given the upside risks to inflation, vigilance is warranted against any emerging inflationary pressures.
“A range of reforms and initiatives has been introduced in recent years to spur productivity and competitiveness—including the adoption of the Business Facilitation Act, finalization of the Financial Sector Blueprint, and programs to support youth skill development, small-scale entrepreneurs, and female labor force participation. Improvement in the World Bank’s Doing Business 2019 indicator is encouraging. Coordination and synergies between the various reforms and initiatives, as well as interaction among the stakeholders, could however be strengthened to enhance their effectiveness and efficiency.
“The mission welcomed the authorities’ ongoing efforts to strengthen the AML/CFT framework in line with the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations and reiterated the need for maintaining strong and independent institutions to overcome the range of policy challenges Mauritius faces to remain an attractive investment destination.
“The mission team expresses its gratitude to the authorities for the productive discussions, excellent cooperation, and hospitality. The IMF stands ready to assist the authorities in the implementation of their economic program, including through the provision of technical assistance, and looks forward to continuing fruitful policy dialogue.”
The mission met with the Prime Minister and Minister of Finance and Economic Development, Pravind Jugnauth, Minister of Financial Services, Good Governance and Institutional Reforms, Dharmendar Sesungkur, Governor of the Bank of Mauritius Yandraduth Googoolye, the Financial Secretary, Dharam Dev Manraj, and other senior government officials, as well as the opposition leader, representatives of the private sector, academia, civil society, unions, and the donor community.